I seem to be on a roll of adding to the diverse range of my previous blog posts. In 2021, I published the first Geographical Misconceptions blog post, and two years later, I published the second. Since it appears it takes me two years to create one of these, which is the same rate at which a Sonic the Hedgehog movie is released, I thought I would continue that tradition.
To recap what I’m talking about when I mention misconceptions, I’m referring to a piece of information that people believe to be true, that in reality is false. But before I continue, why should I care about misconceptions that are geographical in nature?
To be honest, some misconceptions are innocent and localised, but others are widespread. When I hear misconceptions, they grind my gears, so the Vulcan part of me is compelled to insert logic into the conversation and to push back against the misconception. 1
The biggest talking point is that I don’t want adults continuing to spread the incorrect information to other adults, but mainly I don’t want children being taught these misconceptions, because they will grow up believing them to be true, have children of their own and continue to spread the misconceptions. That and eating Sour Cream and Chives. Kids need to be aware of the dangers of that flavour, since “Fair is foul, and foul is fair”. 2
So, let’s pull up our socks, step into our gumboots and traverse into the unknown that is a Some Geek Told Me blog post, and discuss some geographical misconceptions that get my undies in a twist. Lead on!

The Amazon is the longest river in the world
Anybody repeating this misconception could be forgiven, because it’s a close call. The Amazon River is one of the longest rivers in the world, spanning a whopping 6,400 km across seven countries in South America. However, this would be a strange misconception if the Amazon were, in fact, the longest river in the world.
The Amazon River is the second-longest river in the world. The gold medal goes to the Nile River, which stretches across 11 African countries, roughly 6,650 km.

I need to add two points to this misconception: Firstly, it’s worth noting that rivers are constantly changing because of different environmental factors, and it can be problematic to decide and identify where a river starts, especially its source.
The second point is that there seems to be a campaign to crown the Amazon as the longest river, because the lengths are disputed, along with the fact that the Amazon has a higher discharge volume. Until the title has officially been stripped from the Nile, it’s still safe to say the Nile is the longest river on the planet.

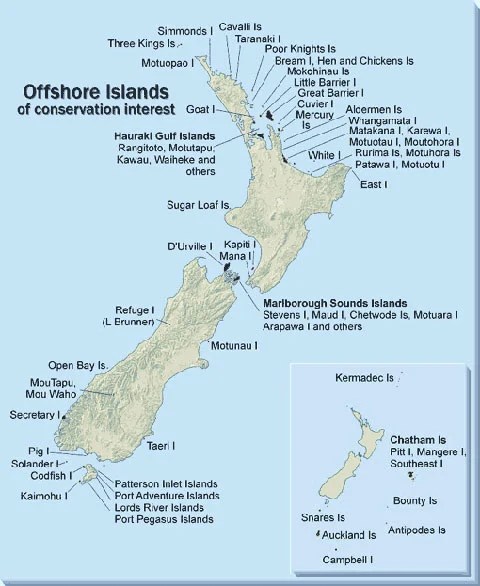
New Zealand is an island/New Zealand only has two islands
I’m obviously biased here, but having lived in other countries, the subject of New Zealand consisting of only one or two islands is not a new misconception to me. Occasionally, the question would come up, and I would have to politely and tactfully explain the truth.
To set the record straight, New Zealand, like many other nations around the globe, is made up of several islands. Granted, the two main islands are the North Island (Te Ika-a-Māui) and the South Island (Te Waipounamu). The South Island is larger, while the North Island holds about 75% of the population.
During the last ice age, about 18,000 years ago, the two islands were connected by a land bridge when sea levels were lower. When the ice age ended, the land bridge was submerged when the sea levels rose, which resulted in the formation of the Cook Strait, the body of water that separates the two islands.
Located off the southern coast of the South Island is Stewart Island (Te Punga o Te Waka-a-Māui), which is the third largest island in the country. New Zealand consists of over 600 islands, including the Subantarctic Islands. Approximately 16 of these islands are inhabited. Therefore, it’s wrong to say that New Zealand has only one or two islands.
Istanbul is the capital city of Türkiye
Can you name any city in Türkiye other than Istanbul? Istanbul is the most well-known Turkish city the world knows, so it has to be the capital city, right? The computer says no. 3
Like many cities on Earth, Istanbul is the most famous city in its country, or even the largest, but these two factors do not automatically mean it’s the capital.
Istanbul has a population of about 15 million, which works out to be roughly 18% of Türkiye’s population, so it is large, but it’s not the capital city; although it was the capital of the Ottoman Empire until 1922. That honour goes to Ankara, with a population of 5.2 million, and it’s been the capital of many empires over the years.
After the Turkish War of Independence and the fall of the Ottoman Empire, the Republic of Turkey was formed. Ankara was officially made the capital on 29th October 1923, since the administration of the country was moved from Istanbul to Ankara.

The Himalayas are the longest mountain range on the planet
This is an easy misconception to believe, because it makes sense that they would be. Firstly, the Himalayas are the world’s highest mountain range, averaging 6,000 to 6,100 m. It’s rather obvious when nine of the ten highest mountains above sea level are found in the Himalayas, especially with Mount Everest, the highest mountain on the planet above sea level, measuring 8,848.86 m.
But, we were asking about the longest mountain range on the planet, were we not? Correct, because it’s not the Himalayas; it’s the Andes. Stretching along South America’s spine, it covers 8,900 km through Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela, and is 200 to 700 km at its widest. The Andes are the longest mountain range above sea level on the planet.
Now, if you were paying attention, I mentioned something odd. Similar to Mount Everest being the highest mountain in the world above sea level, the same can be applied here. The Andes are the longest mountain range in the world, but only above sea level.
The longest mountain range on Earth is actually underwater: the Mid-Ocean Ridge. The Mid-Ocean Ridge is found around the world, as it is interconnected by plate tectonic boundaries. These underwater ridges are part of a global Ocean Ridge system, which covers every ocean.
The mountain range is continuous, and it spans over 65,000 km, making it several times longer than the Andes. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge alone stretches 16,000 km. So to clarify, the Andes are the longest mountain range above sea level on the planet, but the Mid-Ocean Ridge is the longest in total.

The United States of America only borders two countries
This is yet another misconception, which, in my humble opinion, is quite understandable, why people would think this is true. Yes, the United States of America does indeed border two countries, notably two land borders.
The infamous Southern border, where apparently the world’s supply of drug dealers, criminals, rapists, and murderers enters the United States, which borders along the southern end of the continental United States and Mexico.
The Northern border, which you don’t need to be a brain surgeon to understand, shares two borders with Canada. The first and most obvious border is on the northern side of the continental United States. The second border with Canada is shared through Alaska, because, as we all know, “Alaska is part of the United States.”
So, to recap, the United States shares borders with Mexico and Canada, though they are land borders. And this is where the misconception comes into effect, because the United States also has maritime borders, or water borders.
It shares a maritime border with Russia, yes, I said Russia. It’s a de facto boundary between the two countries across the Bering Strait, because of Alaska’s location and position relative to Russia’s easternmost islands.
The United States also have many dependencies, territories and islands in the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea. This results in the United States having maritime borders with The Bahamas, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Japan, Marshall Islands, Kiribati, and Federated States of Micronesia, as well as collective and/or disputed borders with Jamaica, Haiti, Colombia, Honduras, Nicaragua, Samoa, Tonga, Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau, Sint Maarten, the British Virgin Islands, and Anguilla.
Because some of these countries are dependencies and territories of other countries, the United States, by extension, also shares maritime borders with Venezuela, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands.

How did I do with explaining these geographical misconceptions? Do you have any of your own? As always, please let me know.
And that is another blog post for another week. Just to give everybody a heads up, my Christmas break is coming up soon, where I will take the second of my two annual holidays away from New Zealand’s 5th least favourite website. The dates have to be confirmed with the staff, but I’ll let you know soon.
Also, if you can’t back yourself, nobody else will, so in that vein, I would like to remind everybody that my Twitter and Mastodon accounts still exist, so please drop by. I’m aiming to one day get 50 followers on Twitter and 200 followers on Mastodon. I seem to be more popular on Mastodon than Twitter, though the reasons are probably, like Destruction, Desire and Dream, endless.
The 2026 FIFA World Cup and 2027 Rugby World Cup schedules have been recently drawn, so I’m still processing New Zealand’s games in both of these tournaments. I may have to post a reaction to them. Maybe. Are you happy with either draw or Netflix’s monopoly purchase?
Thanks again for reading, following, and subscribing to Some Geek Told Me. Please remember to walk your dog, read a banned book, don’t commit war crimes, and I’ll see you next week.
1. It’s always nice to sneak in a Star Trek reference.
2. Like wise for Shakespeare references as well.
3 In 2022, the government of Turkey officially changed its name to Türkiye, which was adopted by the United Nations.










You must be logged in to post a comment.